-
[Java] Iterable 과 Iterator 이란?Language/Java 2020. 1. 18. 00:02728x90반응형
Collection framework는 뭔가 되게 많고 복잡한 느낌이 들어서 완벽하게 정리가 된 느낌은 아니었다. 가령 Iterator는 어떤 역할인지는 알겠는데 어떤 계층구조를 갖고 있는지 궁금했고, 공부하다보니 Iterable이 있길래 어떤 차이가 있는지도 모르겠어서 정리하려고 한다.
1. Iterable 이란 무엇인가?
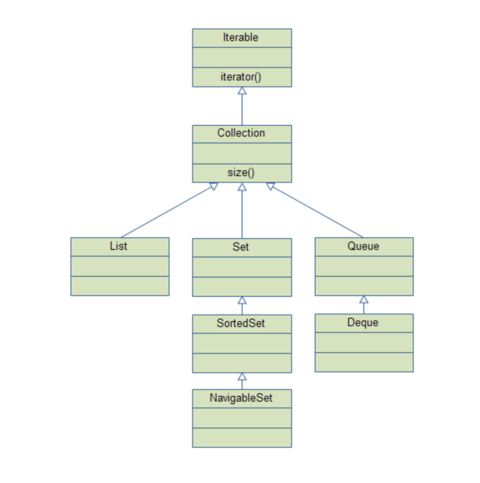
출처 : https://m.blog.naver.com/PostView.nhn?blogId=writer0713&logNo=220877874725&proxyReferer=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.google.com%2F Collection 인터페이스와 List, Set, Queue 인터페이스의 계층구조는 알고 있었지만, Iterable이 Collection의 상위 인터페이스 인지는 잘 몰랐다. 그래서 인텔리제이에서 내부 구현 코드를 확인해봤다.
12345678910public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E> {// Query Operations/*** Returns the number of elements in this collection. If this collection* contains more than <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt> elements, returns* <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt>.** @return the number of elements in this collection*/이렇게 Collection 인터페이스의 상위 인터페이스는 Iterable 이라는 것을 알 수 있다. 그러면 Iterable의 내부를 한번 봐보자.
12345678public interface Iterable<T> {/*** Returns an iterator over elements of type {@code T}.** @return an Iterator.*/Iterator<T> iterator();Iterable 인터페이스 안에는 iterator 메소드가 추상메소드로 선언이 되어있다. 이렇게 때문에 Collection 인터페이스 계층구조에서 List, Set, Queue를 구현하는 클래스들은 다 iterator 메소드를 가지고 있다. 따라서 Iterable의 역할은 iterator()메소드를 하위 클래스에서 무조건 구현을 하게 만들기 위함이다.
2. Iterator 이란 무엇인가?
Iterator 인터페이스는 Collection과는 별개로 존재하는 인터페이스이다.
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142public interface Iterator<E> {/*** Returns {@code true} if the iteration has more elements.* (In other words, returns {@code true} if {@link #next} would* return an element rather than throwing an exception.)** @return {@code true} if the iteration has more elements*/boolean hasNext();/*** Returns the next element in the iteration.** @return the next element in the iteration* @throws NoSuchElementException if the iteration has no more elements*/E next();/*** Removes from the underlying collection the last element returned* by this iterator (optional operation). This method can be called* only once per call to {@link #next}. The behavior of an iterator* is unspecified if the underlying collection is modified while the* iteration is in progress in any way other than by calling this* method.** @implSpec* The default implementation throws an instance of* {@link UnsupportedOperationException} and performs no other action.** @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code remove}* operation is not supported by this iterator** @throws IllegalStateException if the {@code next} method has not* yet been called, or the {@code remove} method has already* been called after the last call to the {@code next}* method*/default void remove() {throw new UnsupportedOperationException("remove");}Iterator 인터페이스의 내부 구현은 위와 같이 되어있다. 따라서 위의 hasNext(), next(), remove() 등의 메소드를 이용할 수 있다. 용도는 컬렉션클래스의 데이터를 하나씩 읽어올 때 사용한다. 표준화가 되어 있지 않다면 컬렉션 클래스의 데이터를 읽어올 때마다 해당 클래스의 데이터를 꺼내오는 메소드들을 다 알고 있어야 하기 때문에 Iterator이 존재한다.
또한 공통 인터페이스를 정의해서 표준을 정의하고 구현하여 표준을 따르도록 함으로써 코드의 일관성을 유지하여 재사용성을 극대화하는 것이 객체지향 프로그래밍의 중요한 목적 중의 하나이다.
123456789101112131415import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.LinkedList;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>();list.add("Lee"); list.add("ekk"); list.add("eww");Iterator it = list.iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {System.out.print(it.next() + " ");}}}예시의 코드와 같은 상황이 있을 때, list.iterator() 의 역할을 생각해보자. 참조변수 list 로 iterator 메소드를 호출했다.
따라서 iterator은 LinkedList의 형태의 Iterator을 반환할 것이다. 그리고 나서 hasNext(), next()메소드를 통해서 출력을 하게 된다.
반응형'Language > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
[Java] Generic 개념 및 정리 (0) 2020.01.22 [Java] equals() 해시코드 비교 및 개념 정리 (0) 2020.01.19 [JAVA] next(), nextLine() 의 차이 (4) 2020.01.16 [JAVA] Array.sort 와 Collections.sort 의 차이 (0) 2020.01.13 [JAVA] ArrayList와 LinkedList의 차이 (6) 2020.01.12